Early Medieval Period in India (650-1206) – History Study Notes & Stuff
After Harshavardhana, new kingdoms and dynasties emerged, they were the prominent zamindars or warriors who emerged around the 7th century. The kings accepted them as Samanthas, and received gifts from these Samanthas, who assisted the kings in their need.
They proclaimed himself Maha-Samanthas (maha-mahadaleshvara). For example, the Rashtrakutas in the Deccan, who were initially under the Chalukyas of Karnataka, gained control of the land in the mid-8th century.
There were Brahmin rulers like Gurjara-Pratihara Harichandra in Rajasthan and Kadamba Mayurasharman in Karnataka.
The "Tripartite struggle" for the supremacy among the Palas, Partihara and rashtrakutas was the major event in these centuries. The main reason for this struggle was the desire to possess kannauj city of Uttar pradesh.
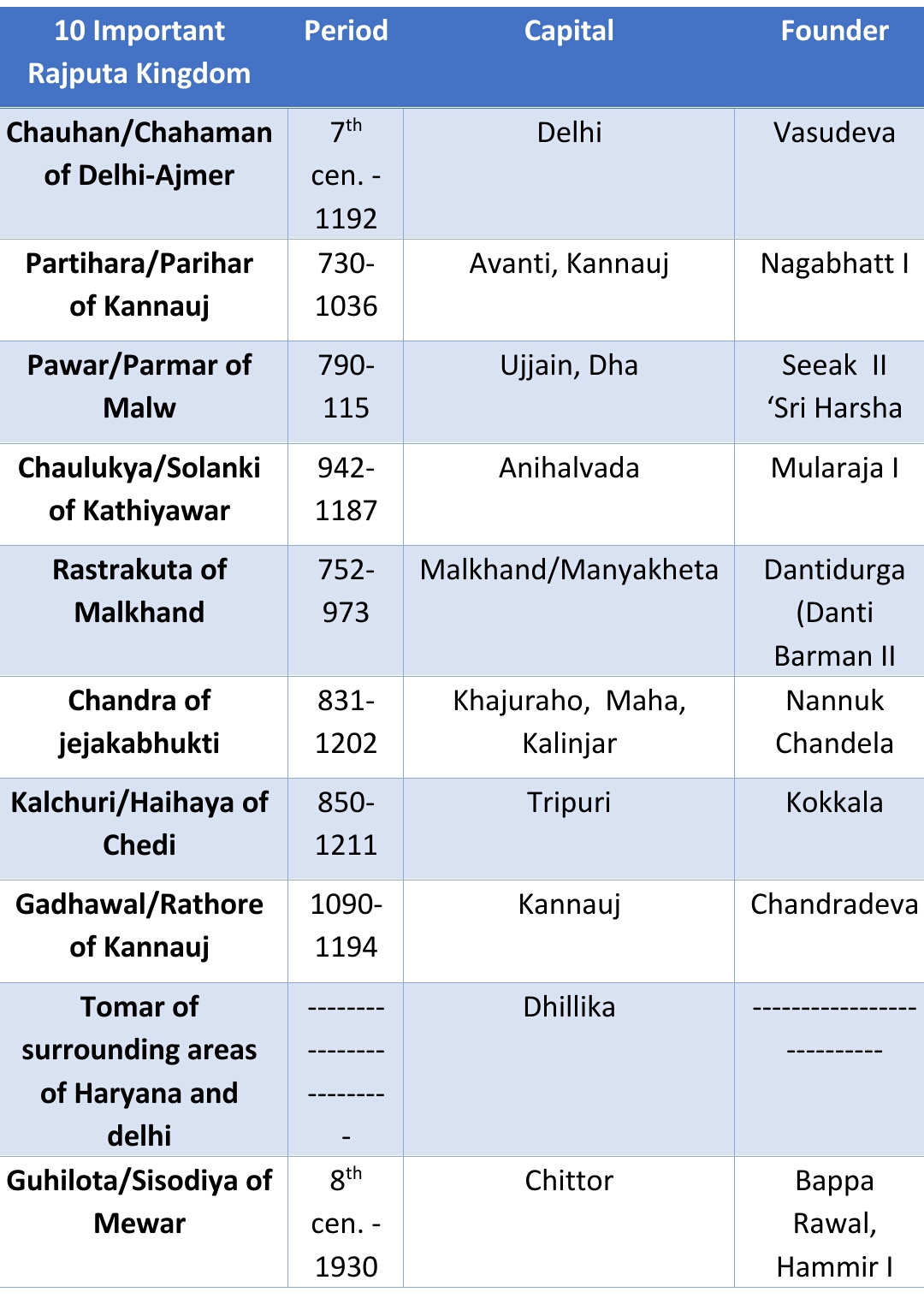
Generally, the period between 650 AD to 1206 AD is called Rajput period. This period was characterized by a lack of unity among states between foreign invasions.
The Pala dynasty of Bengal during Early Medieval Period in India:
The Pala empire was founded by Gopala in 750 AD. His son Dharmpala (770-810) succeeded him, who revived Nalanda University. He also founded the Vikramshila University.
Dharmapala was succeeded by Devapal (815-855 AD). He built the popular the Mahabodhi temple at Bodh Gaya. The Palas also patronized Buddhism on the decline in other parts of India. They were the followers of Mahayana and Vajrayana schools of Buddhism, Proto-Bengali literature and art flourished during their rule. Sompura Mahavihara (now in Bangladesh), a UNESCO World Heritage Site, was built during the Palsa reign. They ruled parts of modern day Bengal and Bihar.
The Palas dynasty was succeeded by the Sena dynasty of Bengal. Jayadev was a court poet in the court of Lakshmana Sena, the author of "Geeta Govind".
The Pratiharas dynasty of Kannauj During Early Medieval History of India:
The pratiharas also known as Gurjara Pratihara because they probably originated from Gujarat or South-West Rajasthan. Mihir Bhoja (836-882) was the greatest ruler of this dynasty. Kannauj became their capital for some time. They are considered a clan of Rajputs. Nagabhatta was the first great ruler of this dynasty who ruled from about 725 AD to 740 AD. He defeated the Arab Muslim rulers of Sindh and prevented them from occupying Central India. He was succeeded by Devaraja, Vatsaraja and Nagabhatta II. At its peak, the Gurjara-Pratihara Empire included East Punjab, Awadh, Agra, Gwalior and parts of Rajasthan.
Mihir Bhoja 836-882 AD. Reigned, he extended the empire's glory by expanding the boundaries of the empire. Mihir Bhoja made Kannauj an important center in India and maintained a large army. He was a patron of arts and learning. Vaishnavists themselves, they were tolerant of other religions and then Mahendrapal succeeded Bhoja and maintained the empire.
The Rashtrakutas dynasty in Early Medieval Period in India:
Dantiduga was the founder of the Rashtrakuta dynasty, who fixed his capital at Malkhand or Malkhed (Gulbarga district, Karnataka). The famous rock-cut 'Kailash' temple built by Rashtrakutas at Ellora.
Other important Rulers of the time:
The Solankis dynasty of Gujarat in Early Medieval Period in India:
Mulraj I was the founder of the Solanki dynasty. His capital was Anhilwad. Another important ruler of this dynasty was Bhima. He was a witness to the Gujarat invasion under the leadership of Mahmud of Ghazni.
The mighty ruler of the Solanki dynasty was Kumarapala. After his death, the kingdom declined.
The Sisodias dynasty of Mewar in Early Medieval Indian History:
Bappa Rawal was the founder of the Sisodia kingdom. He set up Chittor as his capital. Mewar reached the height of its power under the rule of Rana Kumbha and his grandson, Rana Sanga. Rana Kumbha had defeated the Muslim ruler Mohammad Khilji and erected the Tower of victory (Vijay Stambha) in Chittor. Rana Kumbha successors Rana Sangram Singh (Rana Sanga) and Rana Pratap were also great kings of Mewar.
We hope that this short notes about Early Medieval Period in India is useful for your quick revision. If you want us to add any more details to this article, please do let us know in the comments below.









0 Comments